Archive
เขียนโปรแกรมอย่างไรให้เป็น Thread-safe [ Writing Thread safe code in C# ]
การเขียน multithreading เพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงานให้กับ windows app ต้องระวังเรื่องการเรียกหรือทำงานกับ controls ซึ่งจะต้องตระหนักเรื่อง thread-safe
การเข้าถึง windows forms controls จะไม่เป็น thread-safe ถ้าหาก มี thread 2 threads หรือ มากกว่า เข้าไปเรียกใช้ controls นั้น เพราะมันอาจทำให้ controls นั้น ทำงานหรือแสดงผล ไม่เป็นไปตามที่ คาดหมายไว้ หรือ ที่เรียกว่า inconsistent state ผลก็คือ ทำให้ thread ที่เข้าใช้งาน ได้ผลลัพธ์ที่ไม่ถูกต้อง ทำให้เกิด race conditions และ deadlocks ดังนั้น เราจะต้องมั่นใจว่า การเข้าถึง control นั้นทำในวิธีที่ ปลอดภัย หรือ thread-safe
ใน .NET Framework จะช่วยให้แจ้งเราทราบ หากมีการเข้าถึง control ในลักษณะนี้ โดยแจ้งให้ทราบขณะที่เรา debug โปรแกรม หรือ เรา run โปรแกรมใน debug mode เป็น message ว่า InvalidOperationException แล้วแจ้งชื่อ control name ที่ มีการเข้าถึงจาก thread อื่น ที่ไม่ใช่ thread ที่สร้าง control ที่เกิดปัญหานั้น
ตัวอย่างต่อไป จะเป็นการแสดงให้เห็นถึงการเรียก windows forms controls ในลักษณะที่ เป็น thread-safe และไม่เป็น thread-safe โดยยกตัวอย่าง การ กำหนดค่า Text property ให้กับ TextBox เพื่อแสดงให้เห็นใน สองวิธีการ ตาม code ด้านล่าง
**code ทั้งหมดอ้างอิงจาก msdn.microsoft.com
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CrossThreadDemo
{
public class Form1 : Form
{
// This delegate enables asynchronous calls for setting
// the text property on a TextBox control.
delegate void SetTextCallback(string text);
// This thread is used to demonstrate both thread-safe and
// unsafe ways to call a Windows Forms control.
private Thread demoThread = null;
// This BackgroundWorker is used to demonstrate the
// preferred way of performing asynchronous operations.
private BackgroundWorker backgroundWorker1;
private TextBox textBox1;
private Button setTextUnsafeBtn;
private Button setTextSafeBtn;
private Button setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn;
private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing && (components != null))
{
components.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
// This event handler creates a thread that calls a
// Windows Forms control in an unsafe way.
private void setTextUnsafeBtn_Click(
object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
this.demoThread =
new Thread(new ThreadStart(this.ThreadProcUnsafe));
this.demoThread.Start();
}
// This method is executed on the worker thread and makes
// an unsafe call on the TextBox control.
private void ThreadProcUnsafe()
{
this.textBox1.Text = "This text was set unsafely.";
}
// This event handler creates a thread that calls a
// Windows Forms control in a thread-safe way.
private void setTextSafeBtn_Click(
object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
this.demoThread =
new Thread(new ThreadStart(this.ThreadProcSafe));
this.demoThread.Start();
}
// This method is executed on the worker thread and makes
// a thread-safe call on the TextBox control.
private void ThreadProcSafe()
{
this.SetText("This text was set safely.");
}
// This method demonstrates a pattern for making thread-safe
// calls on a Windows Forms control.
//
// If the calling thread is different from the thread that
// created the TextBox control, this method creates a
// SetTextCallback and calls itself asynchronously using the
// Invoke method.
//
// If the calling thread is the same as the thread that created
// the TextBox control, the Text property is set directly.
private void SetText(string text)
{
// InvokeRequired required compares the thread ID of the
// calling thread to the thread ID of the creating thread.
// If these threads are different, it returns true.
if (this.textBox1.InvokeRequired)
{
SetTextCallback d = new SetTextCallback(SetText);
this.Invoke(d, new object[] { text });
}
else
{
this.textBox1.Text = text;
}
}
// This event handler starts the form's
// BackgroundWorker by calling RunWorkerAsync.
//
// The Text property of the TextBox control is set
// when the BackgroundWorker raises the RunWorkerCompleted
// event.
private void setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn_Click(
object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
this.backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync();
}
// This event handler sets the Text property of the TextBox
// control. It is called on the thread that created the
// TextBox control, so the call is thread-safe.
//
// BackgroundWorker is the preferred way to perform asynchronous
// operations.
private void backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted(
object sender,
RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e)
{
this.textBox1.Text =
"This text was set safely by BackgroundWorker.";
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.textBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox();
this.setTextUnsafeBtn = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.setTextSafeBtn = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.backgroundWorker1 = new System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// textBox1
//
this.textBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(12, 12);
this.textBox1.Name = "textBox1";
this.textBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(240, 20);
this.textBox1.TabIndex = 0;
//
// setTextUnsafeBtn
//
this.setTextUnsafeBtn.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(15, 55);
this.setTextUnsafeBtn.Name = "setTextUnsafeBtn";
this.setTextUnsafeBtn.TabIndex = 1;
this.setTextUnsafeBtn.Text = "Unsafe Call";
this.setTextUnsafeBtn.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.setTextUnsafeBtn_Click);
//
// setTextSafeBtn
//
this.setTextSafeBtn.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(96, 55);
this.setTextSafeBtn.Name = "setTextSafeBtn";
this.setTextSafeBtn.TabIndex = 2;
this.setTextSafeBtn.Text = "Safe Call";
this.setTextSafeBtn.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.setTextSafeBtn_Click);
//
// setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn
//
this.setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(177, 55);
this.setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn.Name = "setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn";
this.setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn.TabIndex = 3;
this.setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn.Text = "Safe BW Call";
this.setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn_Click);
//
// backgroundWorker1
//
this.backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted += new System.ComponentModel.RunWorkerCompletedEventHandler(this.backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted);
//
// Form1
//
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(268, 96);
this.Controls.Add(this.setTextBackgroundWorkerBtn);
this.Controls.Add(this.setTextSafeBtn);
this.Controls.Add(this.setTextUnsafeBtn);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox1);
this.Name = "Form1";
this.Text = "Form1";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
this.PerformLayout();
}
#endregion
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
}
}
จาก code จะเห็นว่ามีการแสดงตัวอย่างการใช้งาน Thread 2 วิธีคือ
1. private Thread demoThread = null; // ใช้ class thread เป็น worker thread
2. private BackgroundWorker backgroundWorker1; // เป็น component ที่ทำงานบน windows form
ซึ่งการ ใช้ class thread นั้นเป็นการสร้าง thread ลูกของ windows form ขึ้นมาอีก 1 thread ซึ่ง worker thread ของ class นี้ จะเกิดสร้างปัญหา
เมื่อต้องเขเาไปเรียกใช้ component ที่วางอยู่บน form ในกรณีนี้คือ TextBox1 เหตุการแบบนี้เรียกว่า ไม่เป็น thread-safe ดังนั้นการเข้าถึงต้องมีวิธีการ เข้าถึงโดยการตรวจสอบ
InvokeRequired ของ textBox1 และ ดำเนินการเข้าถึง แตกแต่างกัน
– ถ้า InvokeRequired = true ให้เข้าถึงโดยใช้ delegate object ผ่าน thread หลักก็คือ Windows form (InVoke)
– ถ้า InvokeRequired = false ให้เข้าถึงได้โดยตรง
ตาม code ที่ตัมานะครับ
private void SetText(string text)
{
// InvokeRequired required compares the thread ID of the
// calling thread to the thread ID of the creating thread.
// If these threads are different, it returns true.
if (this.textBox1.InvokeRequired)
{
SetTextCallback d = new SetTextCallback(SetText);
this.Invoke(d, new object[] { text });
}
else
{
this.textBox1.Text = text;
}
}
ส่วนถ้าเราใช้ background worker ในการทำ multithreading เราก็สามารถเขาถึงได้โดยตรง ผ่าน event run ProgressChanged และ RunWorker conmpleted
ครับ เป็นอันว่าพอสมควรแก่ ประเด็นแล้วนะครับ เพื่อน ๆ ที่เคยเจอปัญหานี้คงพอเข้าใจแล้วนะครับ ขอให้สนุกสนานกับการเขียนโปรแกรม นะครับ
Learn
ํYou ‘ll never be brave if you don’t get hurt
You ‘ll never learn if you don’t make mistake
You ‘ll never be successful if you don’t encounter failure….
– – so
Failure is Success… if you learn from it.
การใช้งาน Deletgate เบื้องต้น
ครับ delegate น่าจะเป็นประเด็นที่ค่อนข้าง จะสับสน กับ นักพัฒนามือหัดขับ หลาย ๆ ท่าน ( ผมด้วย ) ในบทความนี้ จะพูดถึงการใช้งานแบบ พื้นฐานของ delegate เพื่อ พื้นที่สำคัญก้าวต่อไปของ การใช้ delegate ใน C# .net

Delegate เป็น base type ตัวหนึ่งใน .NET ซึ่งมันเป็น class สำหรับการสร้างและใช้ delegate ในขณะ runtime ครับอย่างที่ทราบกันนะครับโดย พื้นฐานแล้ว Delegate คล้ายกับ Function Pointer ใน C++ ซึ่งใช้ในการอ้างอิง method ต่างกันก็ตรงที่ delegate นั้น method ที่จะใช้อ้างอิง ต้องมี หน้าตาเหมือนกับ delegate type ที่ประกาศไว้ หน้าตาเหมือน ก็คือ มี return type และ parameters เหมือน กัน
มีการให้ข้อมูลเรื่องการใช้งาน delegate มากมาย แต่คำถามที่เกิดขึ้นในใจ เพื่อน ๆ ก็คือ การใช้งาน เราจะใช้งานมันเมื่อไร หรือ ความจำเป็นอะไร ที่จะทำให้เราต้องเอา delegate มาแก้ปัญหา หล่ะ แน่นอนครับ มันต้องมีสิครับ ก็คือว่า ในการพัฒนา Application อาจมีบางครั้งหรือบางเหตุการณ์ที่เราอาจ ต้องแก้ปัญหาด้วยการ ส่งผ่าน method ไปให้ กับ method ตัวอื่น เพื่อใช้งาน ( method , function , procedure คืออันเดียวกันนะครับ) ดังนั้นเราก็สามารถใช้ delegate ในการจัดการกับปัญหานี้ได้
เพื่อให้เห็นภาพ วิธีที่ดีก็คือ ดูจากตัวอย่างครับ ตัวอย่างนี้ยืมมาจาก นี่ครับ http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/900fyy8e%28v=vs.71%29.aspx
จากภาพ ในขั้นตอนแรก ก็คือการ ประกาศ delegate ชื่อว่า MyDelegate มี parameter ตัว คือ I เป็น integer และ ไม่มี return type คือ กำหนดให้เป็น void
ต่อไป เป็นการ สร้าง function ชื่อว่า DelegateFunction ซึ่งเป็น ฟังก์ชันที่จะให้ delegate object มาใช้ หรือชี้มาที่ function นี้ จะเห็น ว่า มี parameter และ return type เหมือน กับ delegate ที่ประกาศไว้ นะครับ
ต่อไปเป็นการนำไปใช้ ในขั้นตอนที่ 3 เราส่งผ่าน delegate ให้กับ TaskADelegate fucion โดยผ่านเป็น parameter type เป็น delegate ที่ประกาศไว้
และสุดท้าย TaskADelegate function ก็ถูกเรียกใช้ใน public static void Main() จากคำสั่งนี้ TaskADelegate(new MyDelegate(DelegateFuction));
จากคำสั่งที่เห็น รวบรัดไปหน่อยสำหรับ มือใหม่ ขอแตกออกเป็น 2 คำสั่งดังนีครับ
MyDelegate delCall = new MyDelegate(DelegateFunction);
TaskADelegate(delCall);
จะเห็นว่าเหมือนการสร้าง object นะครับ delCall เป็น object ของ MyDelegate และ ชี้ไปที่ DelegatFunction แล้วก็ส่งผ่านไปให้ function TaskADelegate เรียกใช้ งานอีกที หรือ จะเรียก delCall( ตัวเลขใด ๆ ) เหมือนเรียกใช้ function เลยก็ได้ แล้วแต่การใช้งานครับ
ตัวอย่าง ง่าย ๆ ที่แสดงถึงการใช้ประโยชน์ Delegate คือ การที่ 2 delegate นำมา combine กันได้ หรือมารวมกันได้ โดยใช้ operator + หรือ – 
รูปนำมาจาก http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/900fyy8e%28v=vs.71%29.aspx
1 จากรูปตัวอย่าง เราประกาศ delegate ชื่อว่า myDelegate มี parameter ชนิด string และไม่มี return type
2 ใน class ประกาศ method ที่มี signature เดียวกับ delegate มี 2 function คือ Hello และ Goodbye ทั้งสอง พิมพ์ ตัวอักษร ออกหน้าจอ ว่า Hello, “xxx” และ Good bye , “xxx” ตามลำดับ
3 หลังจากนั้นใน function main เราประกาศ ตัวแปร delegate a,b,c,d
– ให้ a point ไป Hello
– ให้ b pointไป Goodbye
– และ c = a + b;
– และ d = c – a;
ผลการ run จะเห็นว่า เมื่อสั่ง c(); จะมี การทำงาน ของ a() ต่อด้วย b()
เช่นเดียวกันกับ d() จะมีแค่ การทำงานของ b() เนื่องจาก ได้ลบ การทำงาน ของ a() ไปแล้ว
สรุปก็คือ instance ของ delegate สามารถนำมา บวกและ ลบกันได้ โดยที่บวก เป็นการเอา function มาทำงานต่อกัน และ – เป็นลบส่วนการทำงานของ function ที่ลบออกไป ครับ เราอาจใช้
c += a; ก็ได้นะครับ นั่นเป็นวิธีการใช้ delegate แบบพื้น นะครับ ในบทความถัดไป จะพูดถึงการใช้งาน ขั้นสูงขึ้นต่อไปนะครับ s_teerapong2000@yahoo.com
การสร้างตารางข้อมูลแบบ Hierarchy Data Structure เพื่อใช้กับ Treeview control
Treeview control เป็น control ที่ใช้บ่อยกับงาน Interface ที่แสดงข้อมูลในรูปแบบที่เป็น ระดับสัมพันธ์ กันหรือเรียกว่า Hierarchy Data Structure ซึ่งเป็นโครงสร้างแบบเดียวกับ Tree สำหรับ ผู้พัฒนาในระดับต้น มักต้องประสบปัญหาความยุ่งยากเมื่อนึกถึงโครงส้รางแบบนี้ ลองมาดูวิธีการตัวอย่างนี้เป็น แนวทางในการ ในการนำไปประยุกค์ใช้งานต่อไปนะครับ
ความต้องการในการใช้งาน หรือ Business Requirement
ตัวอย่างข้อมูลที่ต้องแสดงในลักษณะนี้ ก็อย่างเช่นการแสดงรายการสินค้าภายใต้กลุ่มสินค้าต่าง ๆ ซึ่งในบ้างครั้งการสร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูล ก็เป็นเรื่องท้าทายให้คิดนะครับ เนื่องจากข้อมูลที่เราใช้งานนั้นมีความเปลี่ยนแปลงเกิดขึ้นได้ตลอดเวลา รูปแบบโครงข้อมูลแบบได้ถึงจะเหมาะสมในการเก็บข้อมูลในลักษณะนี้ สำหรับมือเก่า ๆ ชั้นลายครามอาจจะมองดูว่า เป็นเรื่องหมูตุ๋น งายเสียนี่กระไร แต่มือใหม่หัดขับก็อาจจะมึน ๆ เมื่อเจอโจทย์แบบนี้นะครับ ลองพิจารณาดู จากภาพด้านล่างนี้นะครับ หากต้องการ เก็บข้อมูลและแสดงข้อมูลในรูปแบบนี้ โดยให้ข้อมูลอยู่ในฐานข้อมูล สามารถแก้ไขเปลี่ยนแปลงได้เราจะทำกันอย่างไร
การแก้ปัญหา
– สร้างโครงสร้างข้อมูลให้ได้ตาม รูปแบบที่ต้องการ (Hierarchical data)
– สร้าง logic ในการอ่านข้อมูล (Recursive Funciton)
– ส่งแสดงใน Treeview
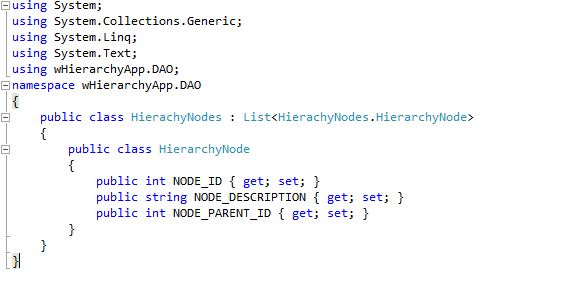
โครงสร้างข้อมูลตัวอย่าง จากรูปด้านล่าง เรามี ตารางข้อมูล ทีมี field เป็น NODE_DESCRIPTION , NODE_ID, NODE_PARENT_ID
ให้ NODE_PARENT_ID เป็นข้อมูลบอก ว่า recode ไหน ที่เป็น parent ของมัน โดยดูที่ NODE_ID ครับ เท่านี้เราก็สามารถที่จะมีโครงสร้างตารางข้อมูล ที่จะแสดง กับ TreeView ได้แล้วนะครับ ซึ่งก็จะได้โครงสร้างดังนี้นะครับ
[ตารางชื่อ tblHierarchyTree – SqlServer Express 2005]
ต่อมา สร้าง Data Access ให้กับข้อมูลข้างต้นนะครับ
– สร้าง class ไว้เก็บค่าจากตาราง ให้ชื่อว่า HierarchyNode
– List ของ HierarchyNode เป็น class ชื่อ HierarchyNodes [สังเกตว่าเติม s นะครับ ]
*จาก code ตัวอย่างอาจจะดู รวบรัด มือใหม่อาจจะงง ก็แยก class HierarchyNode ออกจาก HierachyNodes ก็ได้ครับแล้วค่อย ทำเป็น List ทีหลัง ให้เป็น file ชื่อ HierarchyNode.cs
หลังจากนั้น แล้วทำ Data Access Class เพื่ออ่านค่าจาก ตาราง tblHierarchyTree ตาม code ด้านล่างนะครับ

ผมให้ class ชื่อว่า HierarchyNodeADO นะครับ เต็ม ๆ จะได้ดังนี้นะครับ ไฟล์ชื่อ HierarchyNodeADO.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace wHierarchyApp.DAO
{
public class HierarchyNodeADO
{
string connetion = @"Server=.\SQLEXPRESS; User Id=sa;Password=pongratee;Database=test" ;
public HierachyNodes getAllNODE2()
{
string sqlstr = "Select * from tblHierarchyTree order by NODE_ID";
HierachyNodes result = new HierachyNodes();
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(connetion))
{
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand();
cmd.Connection = con;
cmd.CommandText = sqlstr;
SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader();
while (reader.Read())
{
result.Add(new HierachyNodes.HierarchyNode()
{
NODE_ID = int.Parse(reader["NODE_ID"].ToString()),
NODE_DESCRIPTION = reader["NODE_DESCRIPTION"].ToString(),
NODE_PARENT_ID = int.Parse(reader["NODE_PARENT_ID"].ToString())
});
}
}
return result;
}
}
}
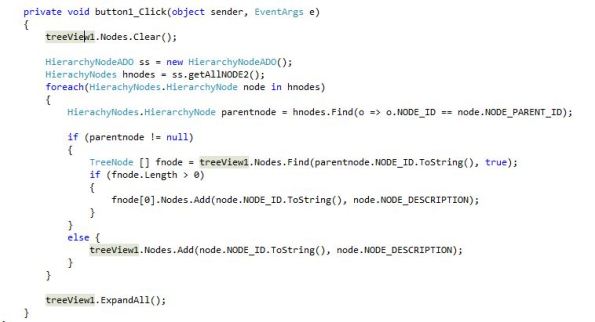
หลังจากนั้นเราก็ เปิด Form1.cs หรือ สร้างในชื่อใด ๆ ก็ได้นะครับแล้ว ก็ วาง Treeview contrl และ button ลงไปครับ
Treeview สำหรับการแสดงผล ส่วน Button สำหรับการ สั่งให้ดึงค่าจาก ตารางมาแสดงผลนะครับ ดู code ด้านล่างเป็นส่วนที่ สำคัญสำหรับการแสดงผลนะครับ ลองดู logic ของ code และทำความเข้าใจดูนะครับ ตรงไปตรงมาไม่ยากนะครับ ผมละส่วนอื่น ไว้ในฐานที่เข้าใจนะครับ code ส่วนนี้จะเป็นส่วนที่ ดังข้อมูลจาก DataBase มาแสดงผลผ่าน HierarchyNodeADO class [Data access class]
s_teerapong2000@yahoo.com
ข้อแตกต่างระหว่าง Int32.Parse(), Convert.ToInt32(), and Int32.TryParse()
 การใช้งานการแปลงค่าข้อมูลจาก string ไปเป็นค่าอื่น ๆ เช่น Integer นั้นจะพบว่า มี method ให้เราใช้งานหลายตัว เราก็เลือกใช้ไปตามชอบแต่ทราบหรือไม่ครับว่า ข้อแตกต่างในการใช้งาน เป็นอย่างไร เราควรเลือกใช้อะไรดี มีคำตอบดี ดี ให้ดังนี้ ครับ Credit : http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/32885/Difference-Between-Int32-Parse-Convert-ToInt32-and Int32.Parse (string s) ใช้แปลง string ที่แสดงตัวเลข integer 32 bit signed
การใช้งานการแปลงค่าข้อมูลจาก string ไปเป็นค่าอื่น ๆ เช่น Integer นั้นจะพบว่า มี method ให้เราใช้งานหลายตัว เราก็เลือกใช้ไปตามชอบแต่ทราบหรือไม่ครับว่า ข้อแตกต่างในการใช้งาน เป็นอย่างไร เราควรเลือกใช้อะไรดี มีคำตอบดี ดี ให้ดังนี้ ครับ Credit : http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/32885/Difference-Between-Int32-Parse-Convert-ToInt32-and Int32.Parse (string s) ใช้แปลง string ที่แสดงตัวเลข integer 32 bit signed
- ถ้าค่า s เป็น null จะ throw ArgumentNullException
- ถ้าค่า s เป็นค่าอื่น จะ throw FormatException
- ถ้า ค่า s เกิน MinValue และ MaxValue จะ throw OverflowException
ตัวอย่าง
string s1 = “1234”;
string s2 = “1234.65”;
string s3 = null; s
tring s4 = “123456789123456789123456789123456789123456789”;
int result;bool success;
result = Int32.Parse(s1);//– 1234
result = Int32.Parse(s2); //– FormatException
result = Int32.Parse(s3);//– ArgumentNullException
result = Int32.Parse(s4); //– OverflowException
Convert.ToInt32(string s) ใช้แปลง string ที่แสดงตัวเลข integer 32 bit signed ให้เป็นตัวเลข
- ถ้าค่า s เป็น null จะ ได้ค่าเป็น 0
- ถ้าค่า s เป็นค่าอื่น จะ throw FormatException
- ถ้าค่า s เกิน MinValue และ MaxValue จะ throw OverflowException
result = Convert.ToInt32(s1); //– 1234
result = Convert.ToInt32(s2);//– FormatException
result = Convert.ToInt32(s3);//– 0
result = Convert.ToInt32(s4); //– OverflowException
Int32.TypParse(string s,out int) ใช้แปลง ค่า string ที่แทนตัวเลข integer 32 bit ให้กับ out variable และ return true ถ้าแปลงได้ และ false ถ้าแปลงไม่ได้
- ถ้าค่า s เป็น null out จะ ได้ค่าเป็น 0
- ถ้าค่า s เป็นค่าอื่น จะให้ค่า out เป็น 0
- ถ้าค่า s เกิน MinValue และ MaxValue จะ ให้ค่า out เป็น 0
success = Int32.TryParse(s1, out result); //– success = true; result => 1234
success = Int32.TryParse(s2, out result); //– success = false; result => 0
success = Int32.TryParse(s3, out result); //– success = false; result => 0
success = Int32.TryParse(s4, out result); //– success => false; result => 0
กล่าวโดยสรุป Convert.ToInt32 ดีกว่า Int32.Parse เพราะ ให้ค่า 0 แทนการ throw exception แต่การใช้งานนั้นก็สามารถเลือกใช้ตามความเหมาะสมนะครับ TypeParse อาจจะเป็นตัวเลือกที่ดีที่สุด เพราะ ตัวมันเองจัดการกับ exception หมดแล้ว Credit : http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/32885/Difference-Between-Int32-Parse-Convert-ToInt32-and